Circular Gauge Pointers
Overview
Pointers on Gauges are special signs for showing your gauges' values. You can even create pointers that will be updated dynamically - manually or programmatically. See Interactive gauges for more. Pointers are a large separate object and have lots of nodes that determine their visual appearance and behavior on the gauge. For example you can totally change the look of pointers, assign attributes or actions to them, bind them to a certain axis and so on. Almost always pointers are a "must-have" element on your gauge.
Types of pointers
In AnyChart Horizontal Gauges we have 3 types of pointers: Bar Pointer, Knob Pointer and Marker Pointer. Here are descriptions for all of them:
Needle Pointer
Needle pointer is usually used to imitate a thin arrow, usually used in clock or in a speedometer. You can totally change its shape and behavior:
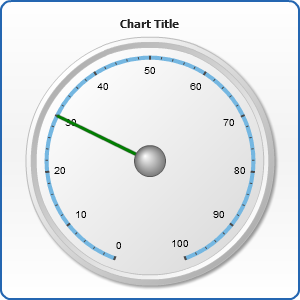
Here is a Needle Pointer Style Tutorial with thoroughly examining its attributes.
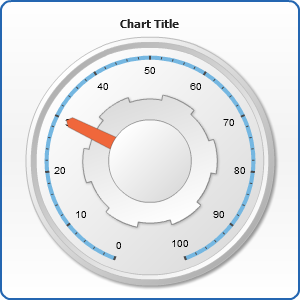
Knob Pointer
Knob pointer is like a needle pointer but it has a cap of larger radius that imitates a gear and may use a custom marker as a needle. With the help of knob pointer you can imitate a massive gear or a volume control.
Marker Pointer
Marker pointer uses a figure of certain shape for pointing your axis current values. As well as in case of bar pointer you can use several markers on your gauge:
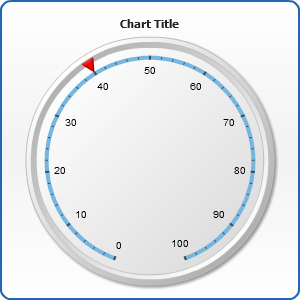
Here is a Marker Pointer Style Tutorial with thoroughly examining its attributes.
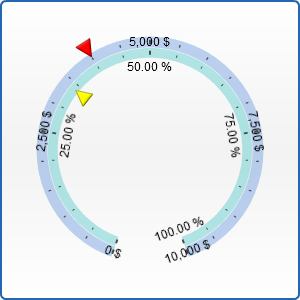
Binding pointers to axes
You can bind a certain pointer or pointers to any axis you want (of course at first you need to define this axes in extra_axes node). To do it just specify the axis attribute of your pointer. If the axis attribute is not specified the pointer is bound to primary axis.
Label
You can add a label to any pointer you want to show your scale value. Label acts as a part of pointer, and you can easily move pointer with it when pointer is editable. Typical XML for label looks like this:
The position subnode attributes have the following values:
| <position> | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Attribute | Values | Default | Description |
| placement_mode | ByPoint | ByRectangle | ByAnchor | Center | Defines the label pointer placement method. |
| halign | Left | Center | Right | Center | Sets horizontal label pointer align. |
| valign | Top | Center | Bottom | Center | Sets vertical label pointer align. |
| padding | Number | Sets the padding for label pointer in percents. | |
| x | Number | Sets the "x" coordinate of your label pointer in percents. | |
| y | Number | Sets the "y" coordinate of your label pointer in percents. | |
| width | Number | Auto | Sets the width of your label pointer. |
| height | Number | Auto | Sets the height of your label pointer. |
| spread | Boolean | False | Sets whether label pointer background is spread to the label pointer container. |
| anchor | LeftTop | CenterTop | RightTop | CenterLeft | Center | CenterRight | LeftBottom | CenterBottom | RightBottom | CenterTop | Sets the anchor point for label pointer. |
Almost all attributes are the same as for Extra labels. Look for the explanation there. The only difference is an "anchor" function. position node has a "ByAnchor" value of placement_mode attribute. If it is "ByAnchor" the label is always positioned at one side of the pointer. The possible anchor values are listed in description of anchor attribute above.
Let's look at the example. We take needle pointer and add label for it. We want to display the value of our label in the upper side of our gauge. XML is as follows:
That's what we get:
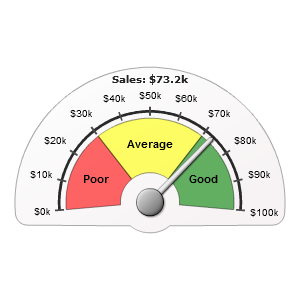
And that's the variant of showing value on the tip of the pointer:
The result:
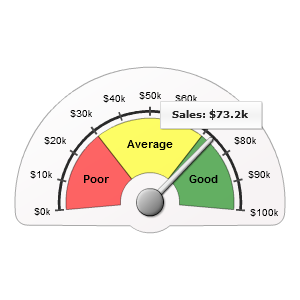
Tooltip
You can add a tooltip to any pointer you want to show value or some other data. Typical XML for tooltip looks like this:
You can disable tooltip, if you don't need it:
